This tool guide is an overview of the GenomeSpace functionality in the user interfaces of the GenomeSpace tools and data sources. This is not meant to be comprehensive documentation for the given tools. For more information on each tool, see the list of GenomeSpace tools and the help links provided on each tool's page.
If you are having problems launching certain desktop tools, which depend on the Java Network Launch Protocol (JNLP), see FAQ2.2 for solutions. These solutions were updated February of 2015, and should take you about five minutes to incorporate. They involve adjusting your browser pop-up blocker and system's Java security exception site list.
For other tool-related documentation, check out the following guides:
Moving Data Between Tools viaGenomeSpace
Project Website: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/
ArrayExpress is a repository of over 30,000 functional genomics experiments comprising nearly 1 million assays. Users can query and retrieve data in a number of different formats including the MIAME and MINSEQE standards.
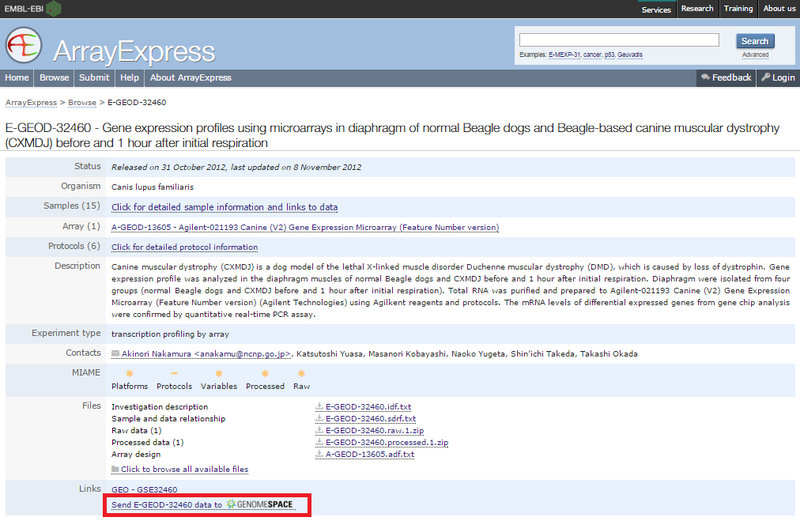
The ArrayExpress detail view for experiments provides a link you can use to send the data associated with that view (IDF, SDRF, and data files) directly to your GenomeSpace account. To do this:

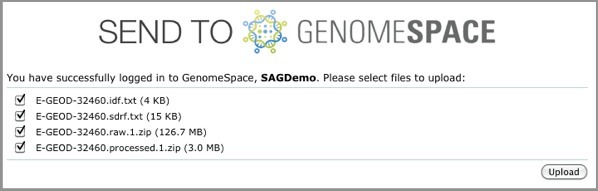
The uploader provides the upload status of each file. When the upload for each file is complete, a green checkmark appears next to the file name. When all the files are uploaded, a message appears to tell you so and also provides a link to GenomeSpace.
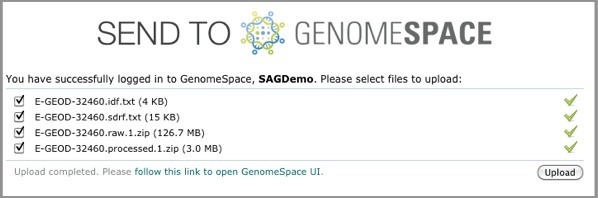
You will find that ArrayExpress has created an ArrayExpress folder in your GenomeSpace cloud storage, with a subfolder that contains the experiment data files. Future ArrayExpress exports will go into the ArrayExpress folder.
Note that ArrayExpress experiment data files are exported from ArrayExpress in MAGE-TAB format.
Read more documentation on how to load data from ArrayExpress into GenomeSpace.
Learn how to send data from ArrayExpress to GiTools using GenomeSpace.
The cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics provides visualization, analysis and download of large-scale cancer genomics data sets.
The cBioPortal "Download Data" tab on the home page provides an option for users to select a published dataset and save the entire file or a subset back to their GenomeSpace account.

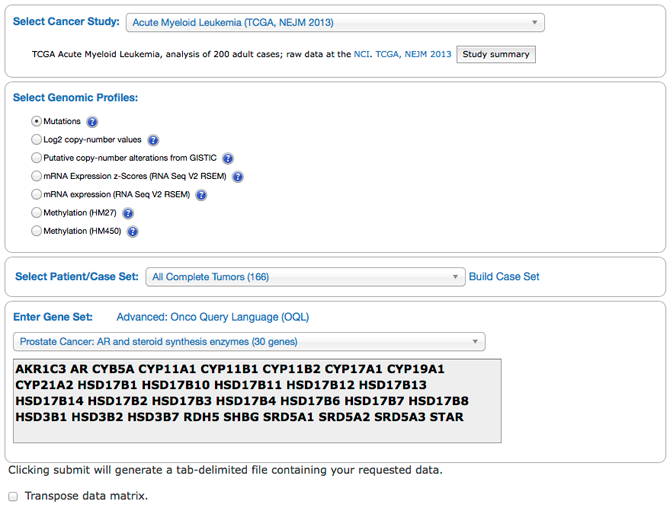

Read more documentation how to load data from cBioPortal to GenomeSpace.
Project Website: http://cistrome.org/ap/
A cistrome is defined as the set of cis-acting targets of a trans-acting factor on a genome scale. The Cistrome project integrates ChIP-chip/seq data for a cistrome with standard analysis pipelines, while providing users with a user-friendly, powerful, flexible web interface with which they can access the data and pipelines.
In addition to the standard Galaxy functions, Cistrome has 29 ChIP-chip- and ChIP-seq-specific tools in three major categories, from preliminary peak calling and correlation analyses, to downstream genome feature association, gene expression analyses, and motif discovery.
Project Website: http://www.cytoscape.org
Cytoscape is an open-source bioinformatics software platform for visualizing molecular interaction networks and biological pathways, and integrating these networks with annotations, gene expression profiles, and other state data. Cytoscape core distribution provides a basic set of features for data integration and visualization. Additional features are available as plugins.
Cytoscape is a Java-based application that downloads to your local machine when you launch it from GenomeSpace. Once it's downloaded to your machine (after a launch from GenomeSpace), you can start it locally (by opening the JNLP) or launch from GenomeSpace. If you launch Cytoscape from the Cytoscape website, at this time it will not be the version that is linked to GenomeSpace.
Like several other applications in the GenomeSpace suite of tools, Cytoscape can be expanded with plug-ins. You can download plug-ins for your Cytoscape by choosing Plugins>Manage Plugins.
Cytoscape has several GenomeSpace menu items.
When you launch Cytoscape from GenomeSpace, your login should be handled seamlessly.
If you start from your GenomeSpace-enabled JNLP of Cytoscape and want to log into GenomeSpace in order to access your Amazon cloud storage or other GenomeSpace tools, you will be asked to log in with your GenomeSpace username and password.
You can also Reset Password on your existing GenomeSpace account.
Clicking File>Import>GenomeSpace provides several options for importing files from GenomeSpace.
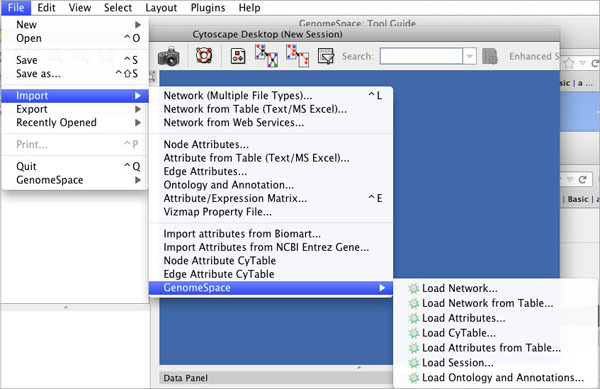
| Load Network | Loads a network from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Load Network from Table | Starts the import from your GenomeSpace cloud storage of a network from a delimited text file or single-sheet MS Excel workbook. |
| Load Attributes | Loads attributes (for node/edge/network) from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. The load dialog allows you to opt to either Load node attributes or Load edge attributes. |
| Load CyTable | Loads a file containing attributes for a CyNetwork from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. The load dialog allows you to opt to either Load node attributes or Load edge attributes. |
| Load Attributes from Table | Starts the import from your GenomeSpace cloud storage of delimited text or single-sheet MS Excel workbook containing attribute data tables that are not formatted into Cytoscape node or edge attribute file formats. |
| Load Session | Loads a CYS file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. A session file (CYS) contains all networks, attributes (for node/edge/network), Desktop states (selected/hidden nodes and edges, window sizes), Properties, some plugin states, and Visual Styles present in a given working state. |
| Load Ontology and Annotations | Loads an annotation/ontology file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. Annotations in Cytoscape are stored as a set of ontologies (a set of controlled vocabulary terms that annotate the objects).The standard file formats used in Cytoscape are OBO and Gene Association. |
Clicking File>Export>GenomeSpace provides options for exporting files to GenomeSpace.
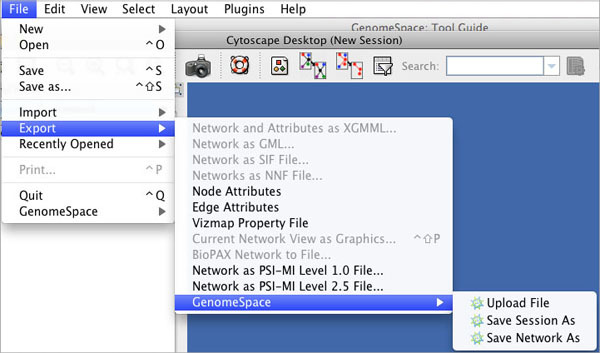
| Upload File | Uploads a file from your local machine to the root level of your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Save Session As | Saves a session file (CYS), containing all networks, attributes (for node/edge/network), Desktop states (selected/hidden nodes and edges, window sizes), Properties, some plugin states, and Visual Styles in your present working state to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Save Network As | Save a network to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
Clicking File>GenomeSpace provides several options for managing your files in your GenomeSpace cloud storage and using GenomeSpace to launch other applications.
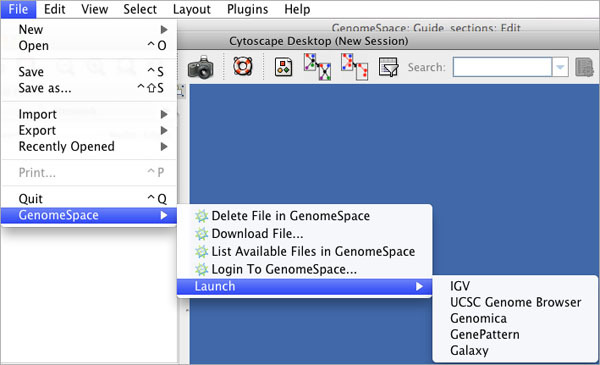
| Delete File in GenomeSpace | Delete a file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Download File | Download a file in your GenomeSpace cloud storage to your local machine. |
| List Available Files in GenomeSpace | Navigate your GenomeSpace directories. |
| Login To GenomeSpace | Log into your GenomeSpace account. |
| Launch | Launch another GenomeSpace tool |
Project Website: http://www.cytoscape.org
New Documentation for Cytoscape 3 is on its way... In the meantime, below is the help from the previous revision (Cytoscape 2.8)
Cytoscape is an open-source bioinformatics software platform for visualizing molecular interaction networks and biological pathways, and integrating these networks with annotations, gene expression profiles, and other state data. Cytoscape core distribution provides a basic set of features for data integration and visualization. Additional features are available as plugins.
Cytoscape is a Java-based application that downloads to your local machine when you launch it from GenomeSpace. Once it's downloaded to your machine (after a launch from GenomeSpace), you can start it locally (by opening the JNLP) or launch from GenomeSpace. If you launch Cytoscape from the Cytoscape website, at this time it will not be the version that is linked to GenomeSpace.
Like several other applications in the GenomeSpace suite of tools, Cytoscape can be expanded with plug-ins. You can download plug-ins for your Cytoscape by choosing Plugins>Manage Plugins.
Cytoscape has several GenomeSpace menu items.
When you launch Cytoscape from GenomeSpace, your login should be handled seamlessly.
If you start from your GenomeSpace-enabled JNLP of Cytoscape and want to log into GenomeSpace in order to access your Amazon cloud storage or other GenomeSpace tools, you will be asked to log in with your GenomeSpace username and password.

You can also Reset Password on your existing GenomeSpace account.
Clicking File>Import>GenomeSpace provides several options for importing files from GenomeSpace.

| Load Network | Loads a network from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Load Network from Table | Starts the import from your GenomeSpace cloud storage of a network from a delimited text file or single-sheet MS Excel workbook. |
| Load Attributes | Loads attributes (for node/edge/network) from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. The load dialog allows you to opt to either Load node attributes or Load edge attributes. |
| Load CyTable | Loads a file containing attributes for a CyNetwork from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. The load dialog allows you to opt to either Load node attributes or Load edge attributes. |
| Load Attributes from Table | Starts the import from your GenomeSpace cloud storage of delimited text or single-sheet MS Excel workbook containing attribute data tables that are not formatted into Cytoscape node or edge attribute file formats. |
| Load Session | Loads a CYS file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. A session file (CYS) contains all networks, attributes (for node/edge/network), Desktop states (selected/hidden nodes and edges, window sizes), Properties, some plugin states, and Visual Styles present in a given working state. |
| Load Ontology and Annotations | Loads an annotation/ontology file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. Annotations in Cytoscape are stored as a set of ontologies (a set of controlled vocabulary terms that annotate the objects).The standard file formats used in Cytoscape are OBO and Gene Association. |
Clicking File>Export>GenomeSpace provides options for exporting files to GenomeSpace.

| Upload File | Uploads a file from your local machine to the root level of your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Save Session As | Saves a session file (CYS), containing all networks, attributes (for node/edge/network), Desktop states (selected/hidden nodes and edges, window sizes), Properties, some plugin states, and Visual Styles in your present working state to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Save Network As | Save a network to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
Clicking File>GenomeSpace provides several options for managing your files in your GenomeSpace cloud storage and using GenomeSpace to launch other applications.

| Delete File in GenomeSpace | Delete a file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Download File | Download a file in your GenomeSpace cloud storage to your local machine. |
| List Available Files in GenomeSpace | Navigate your GenomeSpace directories. |
| Login To GenomeSpace | Log into your GenomeSpace account. |
| Launch | Launch another GenomeSpace tool |
FireBrowse is a companion portal to the Broad Institute GDAC Firehose analysis pipeline, and was developed to cull and analyze data generated by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), which characterizes and identifies genomic patterns in human cancer models. Backed by a powerful compute infrastructure, programming interface, online reports and modern graphical tools, FireBrowse provides a simple yet capable means of visually and programmatically exploring one of the most comprehensive and deeply-characterized open cancer datasets in the world. FireBrowse provides access to a variety of cancer genomics data, such as clinical annotations, DNA copy number, miR, miRseq, mRNA and mRNAseq; as well as a comprehensive suite of more than 100 interdependent analyses of those data, including: correlations, clustering, and GISTIC and MutSigCV. FireBrowse is developed at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard.
More information about FireBrowse can be found using the following links:
When you launch FireBrowse from GenomeSpace, you will be automatically redirected to the FireBrowse front page (http://firebrowse.org/). On this page, you can access FireBrowse data by selecting a cohort.
To do this, you can (A) select a cohort from the drop-down menu; or, (B) simply click on the respective row of the samples barchart for that cohort. In the example below, we will be downloading Breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA) data. Therefore, we can either: (A) “Breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA)” from the drop-down menu; or (B) click on the BRCA barchart.
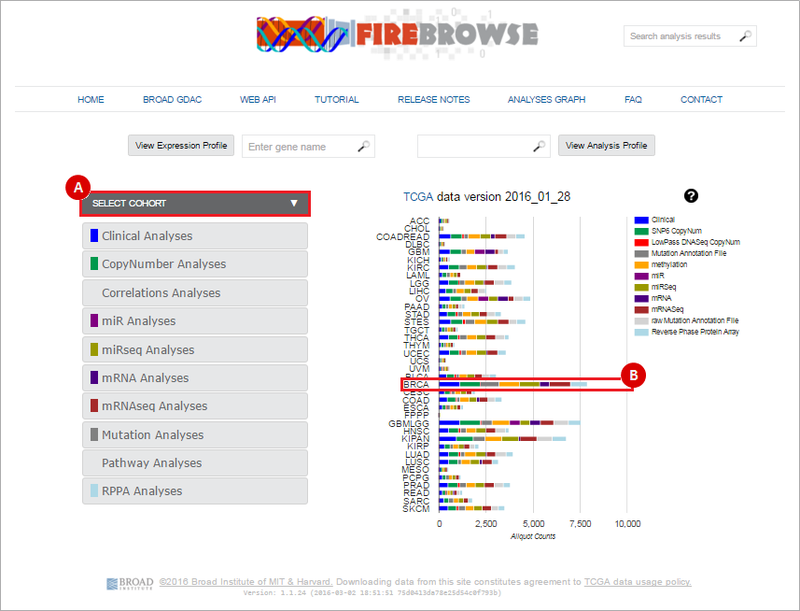
Next, select the data that you wish to download. FireBrowse collects data from a variety of analyses: clinical, copy number, miR, miRseq, mRNA, mRNAseq, mutation and pathway analyses.
To select a data type, either: (A) select the data type from the left-hand menu; or (B) click on the corresponding barchart. In our example, we will download SNP6 Copy Number variation data. We therefore either: (A) Click on the "CopyNumber Analyses" box; or (B) click on the "SNP6 CopyNum" barchart.
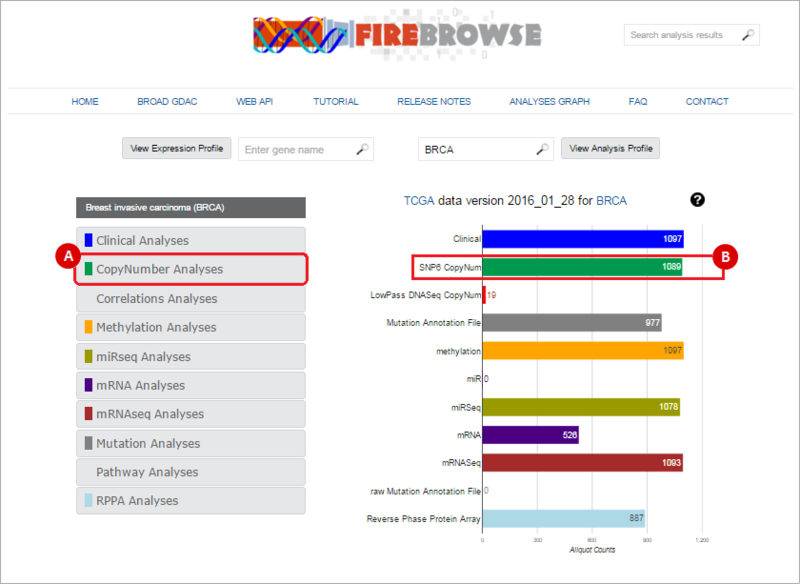
When you select a data type to download, this will prompt a data download interface. To send data to GenomeSpace, use the following method:
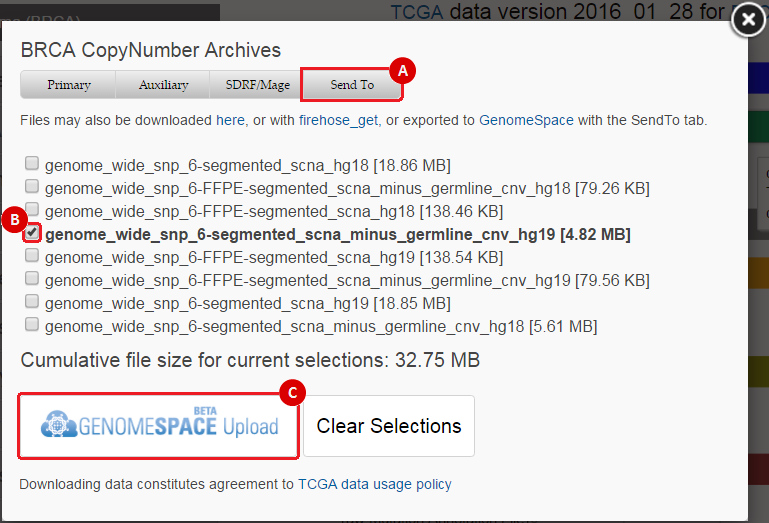
This will prompt you to choose a GenomeSpace directory to save the file(s) to. Once you have chosen a directory, you can click the "Submit" button. This will send the file(s) to your GenomeSpace directory as a .tar.gz file.
When you return to GenomeSpace, you will have to right-click on the file and choose "Expand Archive". This will unzip the .tar.gz file and create a new folder with the same name. The files you chose to download in Step B will be available in that folder.
Project Website: http://galaxyproject.org/
Galaxy is an open-source, scalable framework for tool integration that allows users to analyze multiple alignments, compare genomic annotations, and profile metagenomic samples, among many possible analyses; workflows allow the linking together of analyses.
Please note that during the GenomeSpace Beta, you will be connected with a Galaxy test server.
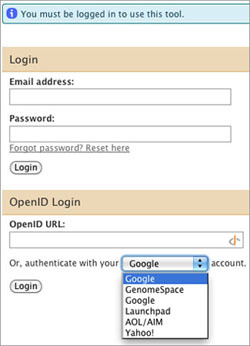
When you launch Galaxy from GenomeSpace, you will see a login window. Do not enter anything in the Email address, Password, or OpenID URL fields!
In the final line under the OpenID login section ("Or, authenticate with your _____ account."), select GenomeSpace and click Login.
Galaxy has its own tools that perform different functions or analyses, and there are tools for interacting with GenomeSpace.
To import data to Galaxy from GenomeSpace, click Get Data in the Tools menu. Under that, select GenomeSpace import from file browser. This opens your GenomeSpace directories. The navigation is a little different here than it is in GenomeSpace, since there is no separate directories pane. Double-click folders to open them, and double-click ..(To Parent) to return to the previous level of the folder structure.
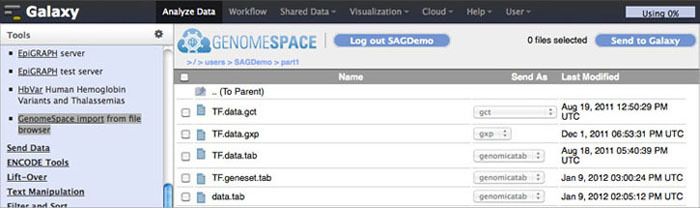
Select the checkboxes for the files you want to bring into Galaxy. You can then select a file format from the file's drop-down menu, if there is a converter. Click the Send to Galaxy button to queue the files for import into Galaxy.
To send data back to GenomeSpace from Galaxy, click Send Data in the Tools menu. Under that, select GenomeSpace Exporter.
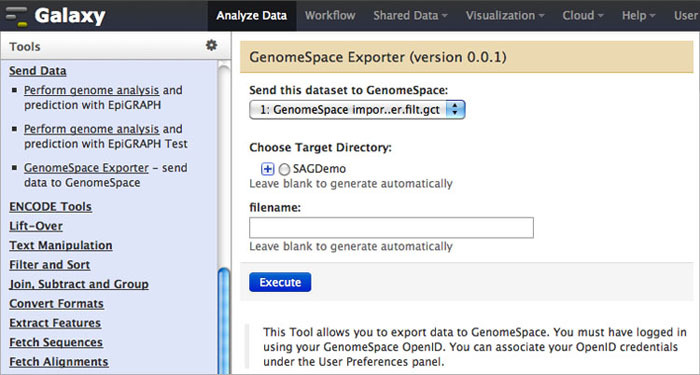
Learn how to send data from Galaxy to IGV using GenomeSpace.
Project Website: http://www.genepattern.org
GenePattern is a powerful genomic analysis platform that provides access to more than 150 tools for gene expression analysis, proteomics, SNP analysis, flow cytometry, RNA-seq analysis, and common data processing tasks. A web-based interface provides easy access to these modules and allows for the creation of multi-step analysis pipelines that enable reproducible in silico research.
A GenomeSpace-enabled GenePattern installation has a number of elements in it that help move data files from GenomeSpace and analysis results to GenomeSpace.
When you launch GenePattern from GenomeSpace, GenePattern allows you to log in using your GenomeSpace account. You will see the GenePattern login screen, and you can click Sign in Using GenomeSpace.
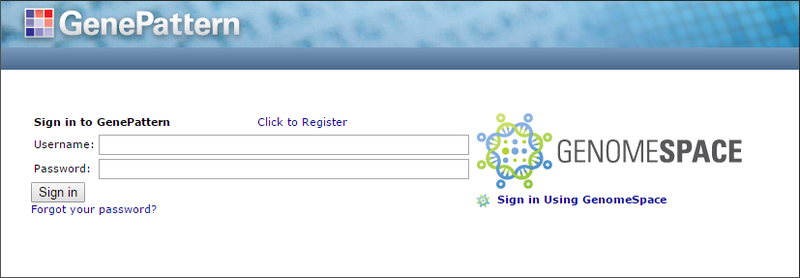
If your GenomeSpace username is not recognized as being associated with any GenePattern username, GenePattern gives you the opportunity to either:
GenePattern receives your files and offers you a number of options of how you would like it to handle those files.
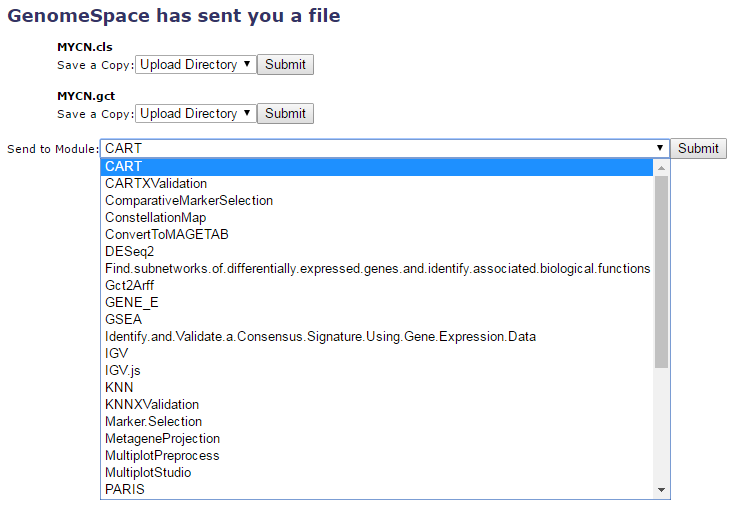
Each file can be saved to the Upload Directory by simply clicking Submit next to the Save a Copy field. Or you can opt to send the file to a module. If the file can be converted by one of the GenomeSpace conversion scripts, you can opt for a conversion as you send it to the module of your choice.
Within the GenePattern UI, the right side of the window is occupied with several tabs that provide access to recently run jobs, uploaded files, and, in GenomeSpace-enabled installations, your GenomeSpace directories. You can navigate these directories.
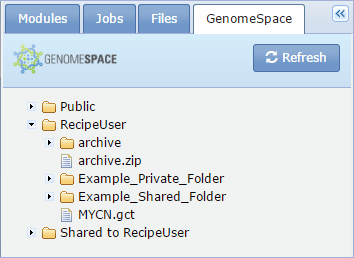
To use one of your GenomeSpace files in a module, drag and drop the name of the file on the field box.
Files in the Job Results and Uploads tabs, as well as on the Job Results page, can be sent directly to GenomeSpace. Click the file name to generate a navigation menu for the file.
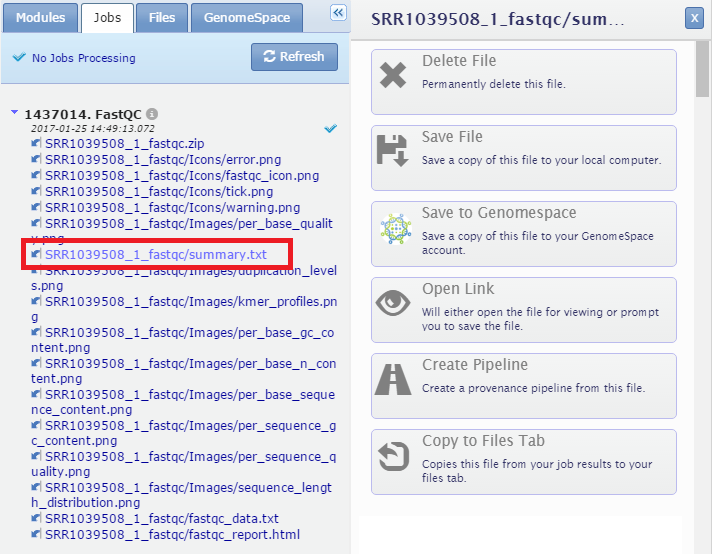
Then, in the drop-down menu, select the location in your GenomeSpace cloud storage where you want to save the file and click Save.
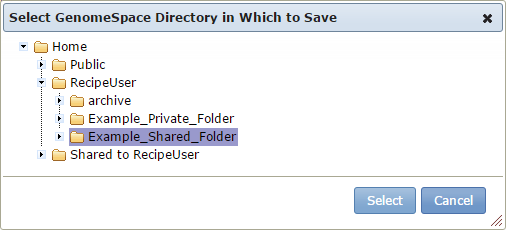
There is also a menu of GenomeSpace functionality, allowing you to log out of GenomeSpace, open GenomeSpace, or go to the GenomeSpace web site.
Learn how to send data from GenePattern to IGV using GenomeSpace.
Learn how to send data from Genomica to GenePattern using GenomeSpace.
Project Website: http://genomica.weizmann.ac.il/
Genomica is an analysis and visualization tool for genomic data that can integrate gene expression data, DNA sequence data, and gene and experiment annotation information.
Genomica is a Java-based application that downloads to your local machine when you launch it from GenomeSpace. Once it's downloaded to your machine (after a launch from GenomeSpace), you can start it locally (by opening the JNLP) or launch from GenomeSpace. If you launch Genomica from the Genomica website, at this time it will not be the version that is linked to GenomeSpace.
When you launch Genomica from GenomeSpace, your login should be handled seamlessly.
If you start from your GenomeSpace-enabled JNLP of Genomica and want to log into GenomeSpace in order to access your cloud storage or other GenomeSpace tools, you need to select GenomeSpace>Login. You will be asked to log in with your GenomeSpace username and password.
Genomica has two menus containing GenomeSpace items.
The GenomeSpace menu in Genomica allows you to interact with your GenomeSpace cloud storage in a number of ways.
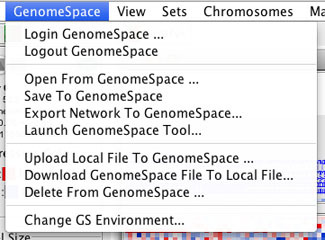
| Login GenomeSpace/Logout GenomeSpace | Signs into or out of GenomeSpace. |
| Open From GenomeSpace |
Opens the GenomeSpace file browser to enable you to open a file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage into Genomica.
|
| Save To GenomeSpace | Saves a file from Genomica to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Export Network To GenomeSpace | Export a network file from Genomica to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Launch GenomeSpace Tool |
Allows you to launch another GenomeSpace-enabled tool from Genomica.
If you click Launch with GS File, the GenomeSpace file browser opens to allow you to select a file to use in launching your selected tool. |
| Upload Local File To GenomeSpace | Uploads a file from your local machine to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
| Download GenomeSpace File to Local File | Downloads a file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage to your local machine. |
| Delete From GenomeSpace | Deletes a file from your GenomeSpace cloud storage. |
The Sets menu contains two GenomeSpace options.
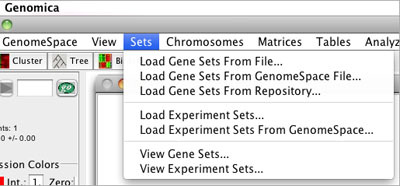
With the Sets menu, you can load either Gene Sets or Experiment Sets from GenomeSpace.
Select Algorithms>Create a Module Network... Under the Regulation tab is a GenomeSpace Load button that enables you to load a list of candidate regulator genes for the analysis.
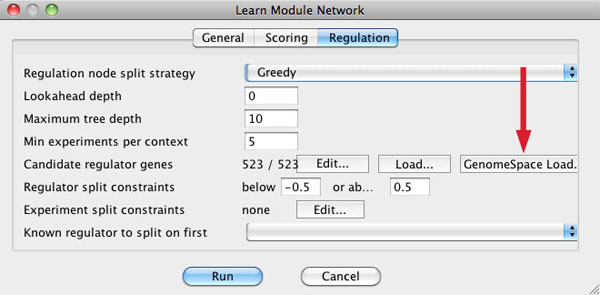
Learn how to send data from Genomica to GenePattern using GenomeSpace.
Project Website: http://wiki.c2b2.columbia.edu/workbench/index.php/Overview
geWorkbench is an open-source bioinformatics platform that offers a comprehensive and extensible collection of tools for the management, analysis, visualization, and annotation of biomedical data. Many kinds of analysis are supported. For microarrays, there are tools for filtering and normalization, basic statistical analyses, clustering, network reverse engineering, as well as many common visualization tools. For sequence data, there are routines such as BLAST, pattern detection, transcription factor mapping, and syntenic region analysis. geWorkbench provides access to a variety of external data sources, including microarray gene expression repositories (caArray), BLAST, gene annotation pages (via caBIO),protein and DNA sequence retrieval, and pathway diagrams (BioCarta), as well as acting a gateway to several computational services currently hosted on Columbia servers and clusters, including Pattern Discovery, Pudge (protein structure modeling), and SkyBase (database of molecular models).
When you launch geWorkbench from GenomeSpace, you will se the Launch geWorkbench dialog.
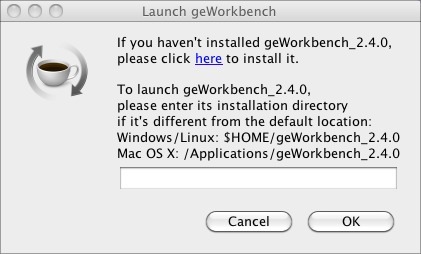
If you have installed geWorkbench in the default location previously, click OK. This will launch geWorkbench.
If you have never used geWorkbench before, or have not used the current version of geWorkbench, you need to install it.
If you have never used geWorkbench before, you can use the prompt you receive when you launch it from GenomeSpace to install it. If you have used it and installed it in a non-standard directory, you can point GenomeSpace to that location in the prompt dialog.
To install geWorkbench:
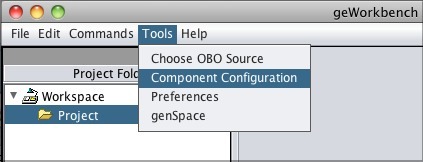
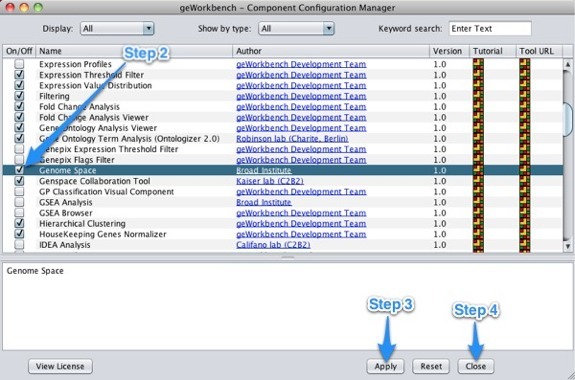
To access GenomeSpace in geWorkbench, enable the GenomeSpace component using the Component Configuration Manager.
|
 |
|
 |
When you click Workspace in the upper left corner of the screen, the GenomeSpace pane will appear to the right.
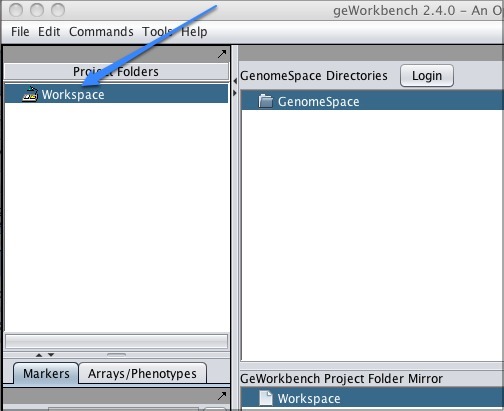
Log in by clicking the Login button next to the GenomeSpace Directories header, and now the GenomeSpace pane will display your directories.
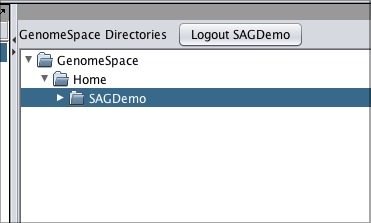
You can work with your files within GenomeSpace:
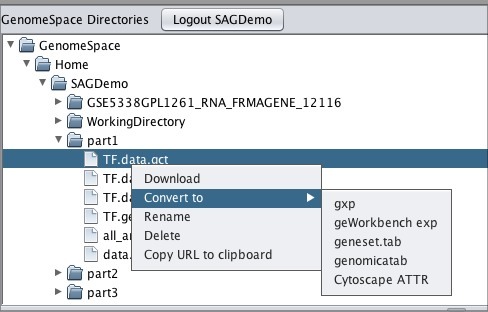
To move one of your GenomeSpace files into geWorkbench:
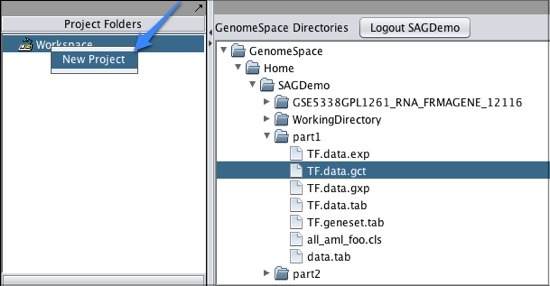
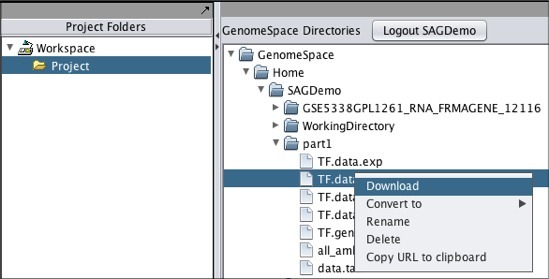
Note that if you download a file that is not in a geWorkbench file format, GenomeSpace will convert it if there is a converter available.
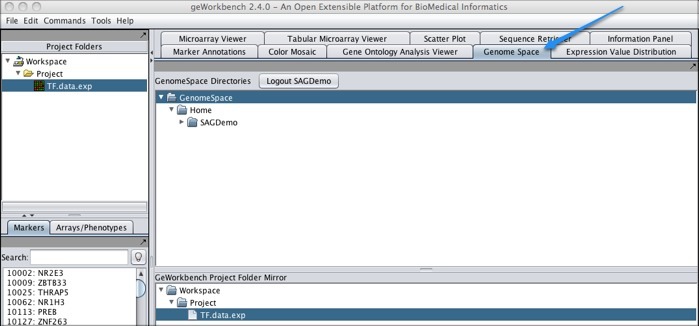
To move files from geWorkbench to GenomeSpace:
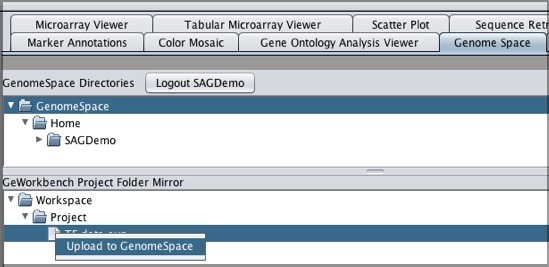
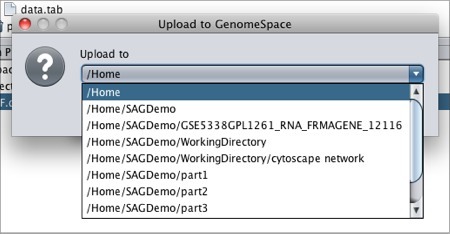
Project Website: http://www.gitools.org/
Gitools is a framework for analysis and visualization of genomic data using interactive heatmaps that also allows data to be imported from various sources, including Biomart, Ensembl, IntOGen, and GenomeSpace.
In the Gitools interactive heatmaps, every cell is associated with one or several values, and users can visualize them and navigate among them. Multiple annotation labels can be added to rows and columns. A number of actions can be performed within the heatmap that help to explore and interpret the data effectively, such as search, filter by value or label, cluster the heat-map, sort rows and columns by different criteria, and more. There are many editable features that make the heatmaps thoroughly customizable, such as color scales, size of cells, grid lines, font size, and color and type for labels.
It is possible to load multidimensional data genomic sets into the heatmaps. For example, a cell in a heatmap that represents a gene in a tumour sample can represent the expression level, mutation status, copy number alterations, and methylation changes. With these properties complemented by a set of analyses (such as correlations, overlaps, enrichment, or group comparison), the exploration of large multidimensional genomics datasets becomes very effective.
To open a data file from GenomeSpace, you can either click the GenomeSpace icon on the Gitools welcome page:

Or by selecting File>Open>Heatmap from Genomespace...
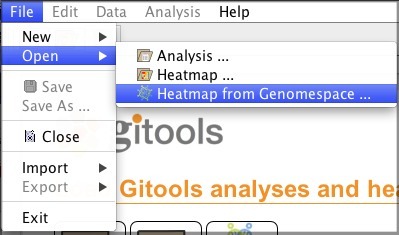
Learn how to send data from ArrayExpress to GiTools using GenomeSpace.
Project Website: http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/
When you launch IGV from GenomeSpace, your login should be handled seamlessly.
When you send to a data file to IGV from GenomeSpace, IGV opens up with the file in the viewer, as shown below. You can then rearrange the data tracks by dragging and dropping them where you want to view them, or otherwise manipulate the view.
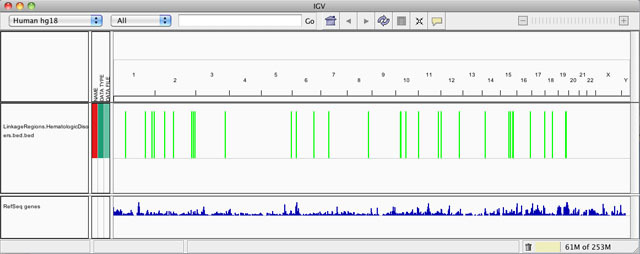
Within the IGV UI, there is a menu for GenomeSpace functionality:
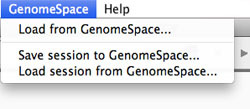
This opens up a dialog box that allows you to load one data file from your GenomeSpace directories in the cloud.
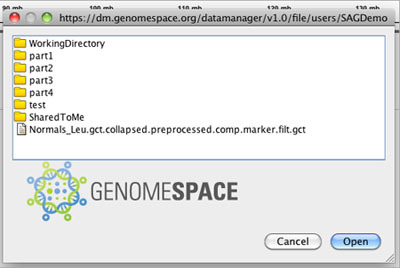
Navigate through the directories and select the file you want to load. Click Open.
A session in IGV is an XML snapshot of the current state of IGV (e.g., the genome that is selected, the data file(s) that is/are loaded into the viewer, the regions of interest that are defined). You can save an IGV session locally normally, but with the GenomeSpace menu, you can save an IGV session to your GenomeSpace cloud storage.
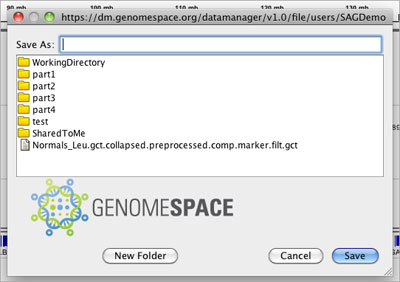
Loading a session file from GenomeSpace is similar to loading a data file, and uses a very similar dialog box.
Learn how to send data from Galaxy to IGV using GenomeSpace.
Learn how to send data from GenePattern to IGV using GenomeSpace.
Project Website: http://isa-tools.org/
The open source ISA metadata tracking tools help to manage an increasingly diverse set of life science, environmental, and biomedical experiments that employ one or a combination of technologies.
When you launch ISAcreator from GenomeSpace, the Java application launches and gives you three options, including GenomeSpace:

Click the GenomeSpace button and you will be asked to log in with your GenomeSpace username and password.

Once you log in, you'll be asked to select a configuration to load. A configuration is a template for describing and curating experiments.
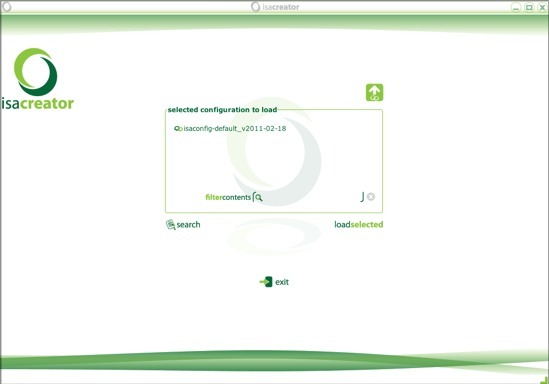
When you have logged in and have your configuration loaded, you can then load ISA-TAB datasets from GenomeSpace. From the main menu, select load an existing isatab file.

Click search genomespace.

In the GenomeSpace dialog, browse to the directory containing your ISA-TAB datasets, select it, and click load selected.
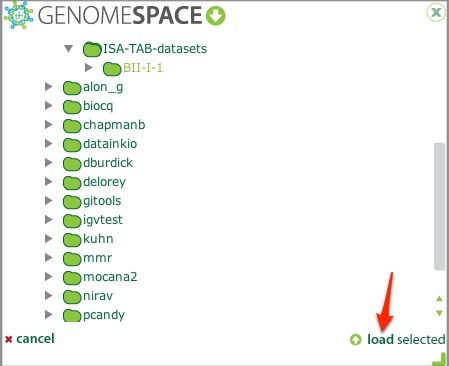
This loads the ISA-TAB files into your investigation.
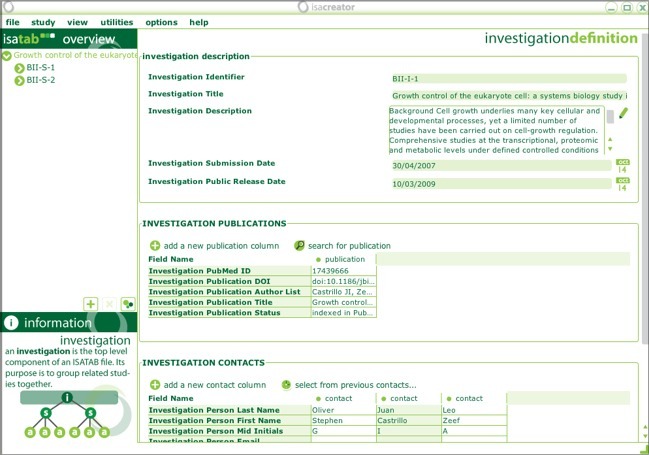
You can save your configuration and ISA-TAB files to GenomeSpace, using either File>save in GenomeSpace or File>save in GenomeSpace as...
For more information on defining your studies, see the ISAcreator User Manual.
Project Website: http://www.broadinstitute.org/msigdb
When you launch MSigDB from GenomeSpace, GenomeSpace tries to log into MSigDB with your email address. If you log in successfully, you will be brought to the Investigate Gene Sets page. Note that MSigDB is closely affiliated with the Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) tool, and thus shares its website. You are in the correct place, even though the logo in the corner says GSEA.
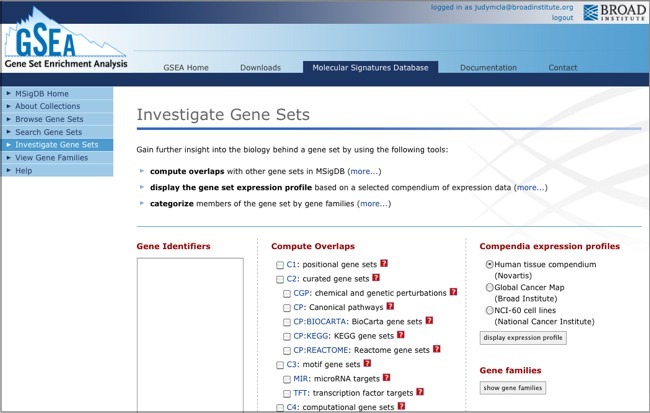
If the email address you use for GenomeSpace is not registered with MSigDB, you will be informed that the login failed. Click the click here link to register as a new user, or log in with a registered email address.
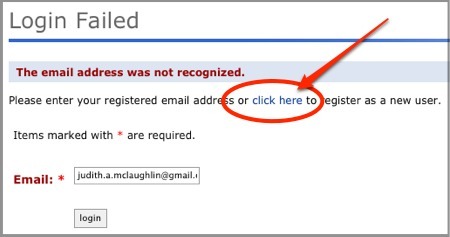
Even if the email addresses are different, as long as you are logged into GenomeSpace and MSigDB concurrently, they can send data to one another.
You can send a list of genes in text format from GenomeSpace to be used as input the MSigDB Online Tools. The list can be one per line, or delimited by spaces, tabs, or commas.
From GenomeSpace, you can:
OR
Your gene list will populate the Gene Identifiers box on the Investigate Gene Sets page.
Note that you can also launch MSigDB by clicking its icon in the tool bar, then paste a list of genes into the Gene Identifier box.
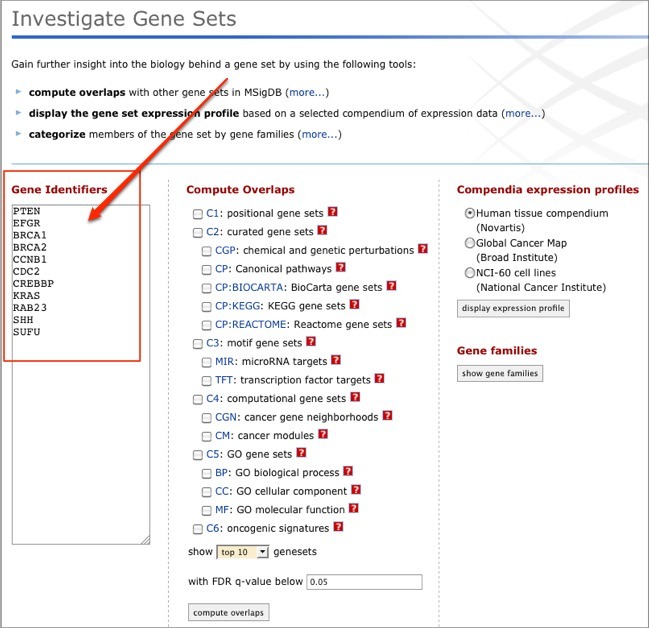
From here, select one or more collections in the Compute Overlaps list and click compute overlaps.
For more information on using the Compute Overlaps tool, see the Compute Overlaps help.
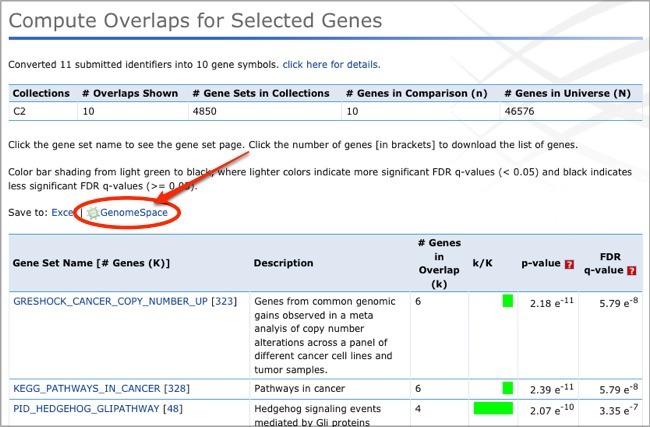
From the Compute Overlaps results page, you can click the Save to: GenomeSpace link to save your results to GenomeSpace.
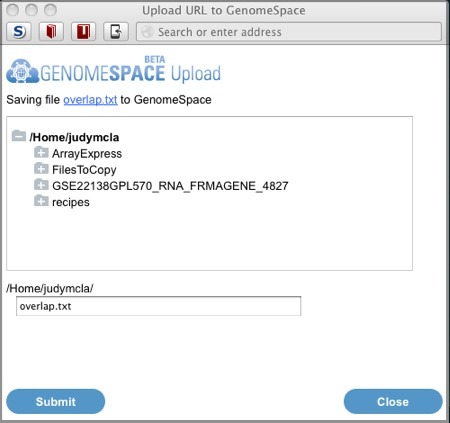
In the dialog, browse to the directory you want to save the overlap file to and click Submit.
Project Website: http://genome.ucsc.edu/index.html
The UCSC Table Browser is a valuable data source linked to GenomeSpace. Since it is a data source, you cannot launch the UCSC Table Browser on a file in GenomeSpace. You can only launch the UCSC Table Browser from its button in GenomeSpace, and then send files from the UCSC Table Browser to GenomeSpace.
The Table Browser allows you to retrieve data associated with a track in text format, to calculate intersections between tracks, and to retrieve DNA sequence covered by a track. After you select the options for your output file, you can opt to send your output file to your GenomeSpace cloud storage. For help using the Table Browser's options, see the UCSC Table Browser documentation.
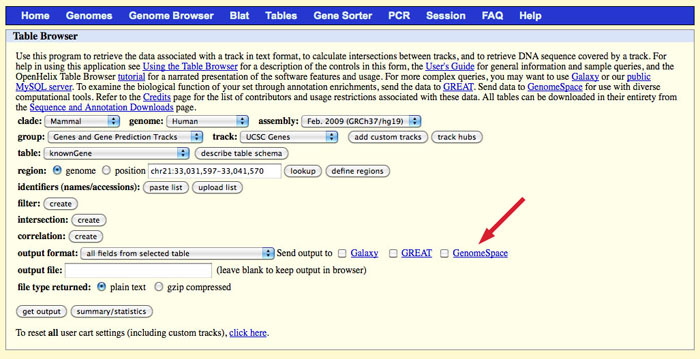
To output your selected track to GenomeSpace, remember to select the checkbox for GenomeSpace.
Select an output format. In the output file field, you need to specify the name of your output file. There are two options for this:
NOTE: You must add the correct extension to your file name. If, for instance, you select BED in the output format drop-down, you will need to add .bed to your output file name. The UCSC Table Browser does not do this for you, and some of the GenomeSpace tools depend on the file extension to determine file type.
When you click get output, you will be asked to log into GenomeSpace, if you have not previously logged in via the UCSC Genome Browser.
After you log in (or if you previously logged in), you will see an uploading message.

Followed by a completion message.
Click Back to return to the Table Browser.
The file you sent to GenomeSpace should appear in your root directory.
Read more documentation on how to load data from UCSC Genome Browser to GenomeSpace.
GSE Identifier: A series record links together a group of related samples, providing a focal point and description for the whole study. Series records may also contain tables describing extracted data, summary conclusions, or analyses. Each series record is assigned a unique and stable GEO accession number (GSExxx).
Module (GenePattern): A module is a discrete portion of code/functionality that is packaged with launch code, UI, and metadata, and can be run within the GenePattern user interface.
The Trinity Cancer Transcriptome Analysis Toolkit (CTAT) aims to provide tools for leveraging RNA-Seq to gain insights into the biology of cancer transcriptomes. Bioinformatics tool support is provided for mutation detection, fusion transcript identification, and de novo transcript assembly. Trinity CTAT was developed at The Broad Institute and is hosted on the Trinity CTAT Galaxy portal by the National Center for Genome Analysis Support (NCGAS) at Indiana University. CTAT is funded by the National Cancer Institute Informatics Technology for Cancer Research (NCI ITCR) program.
More information about Trinity CTAT can be found using the following links:
Before you can launch Trinity from GenomeSpace, you must first sign up for a Trinity account through the National Center for Genome Analysis Support (NCGAS). This can be accomplished by filling out the Trinity Galaxy Registration Form.
Trinity Galaxy support by NCGAS is publically funded, so users are required to sign up and describe the nature of their work and their sources of funding. If you have any questions about this form, please contact the NCGAS team at help@ncgas.org.
Once you have submitted your registration form, you should receive an email from the NCGAS team with your account information and temporary password. This email should arrive within 24 hours of submitting your application.
Once you have signed up for and activated your Trinity CTAT account, you can connect your Trinity account to GenomeSpace using the following method:
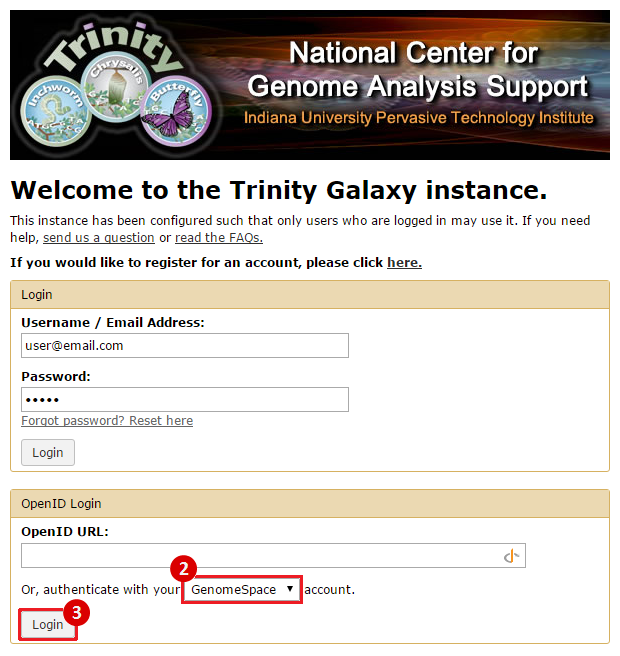
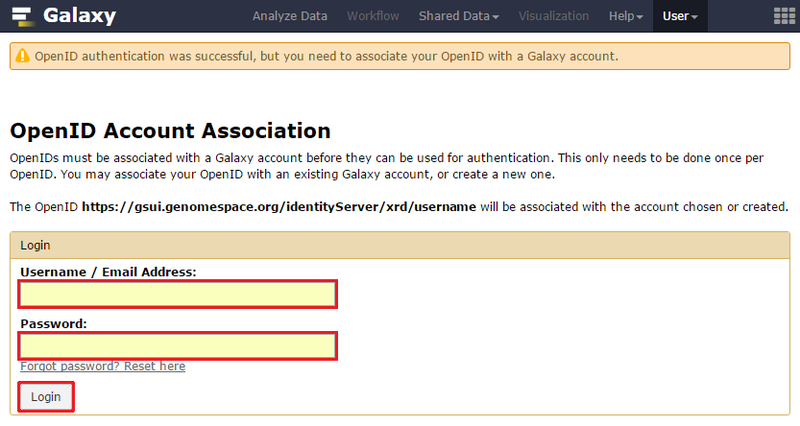
Once you have connected your account, you can begin using Trinity normally.
Trinity encompasses a suite of tools hosted on a Galaxy server. There are three types of tools: (1) tools for interacting with GenomeSpace; (2) auxiliary tools that are common to Galaxy builds; and, (3) Trinity-specific tools which perform different functions or analyses.
To import data to Trinity from GenomeSpace, click Get Data in the Tools menu and select GenomeSpace import from file browser. This opens a view of your GenomeSpace directories. The navigation is a little different here than it is in GenomeSpace, since there is no separate directories pane. Double-click folders to open them, and double-click ..(To Parent) to return to the previous level of the folder structure.
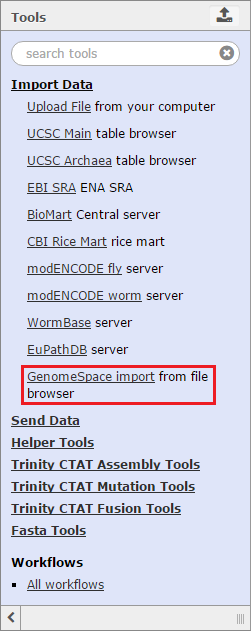
Select the checkboxes for the files you want to bring into Trinity. You can optionally select a file format from the file's drop-down menu, provided there is a converter. Click the Send to Galaxy button to queue the files for import into Trinity.
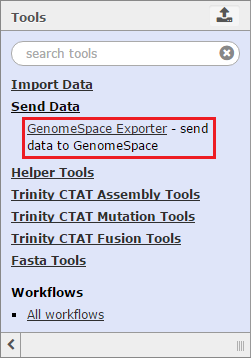
To send data back to GenomeSpace from Trinity, click Send Data in the Tools menu and select GenomeSpace Exporter.

Trinity also has built-in Galaxy tools to help with basic file manipulation and other functions. These tools can by found by clicking on Helper Tools in the Tools menu.
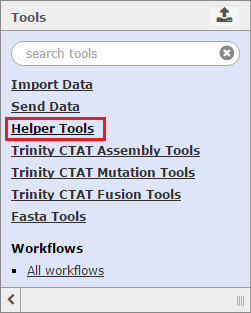
To learn about other Galaxy tools that can be found in Trinity, please visit the Galaxy Wiki Resource.
The Trinity CTAT suite of tools is specific to this build of Galaxy, and is not currently deployed on the main Galaxy server which is also connected to GenomeSpace. Currently, CTAT supports tools and functions for completing analyses such as:
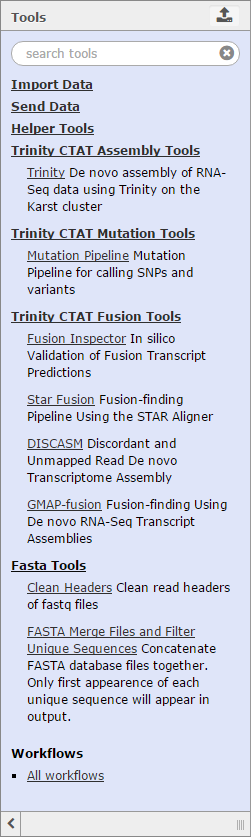
More information about the capabilities of these specific tools can be found on the Trinity CTAT wiki page. In the future, Trinity CTAT may also support lincRNA classification, foreign transcript detection, and single-cell cancer transcriptome analysis.